Technology, Capacity, Quality Standards & Global Market Value
A modern raisin processing plant is the backbone of the global dried fruit industry. From post-harvest grape handling to advanced sorting, grading, and packaging, processing plants determine final product quality, export eligibility, food safety, and market price.
With rising global demand for natural, organic, and value-added raisins, professionally managed processing plants play a crucial role in ensuring consistency, traceability, and scalability for international buyers.
Global Raisin Industry & Processing Market Overview (H2)
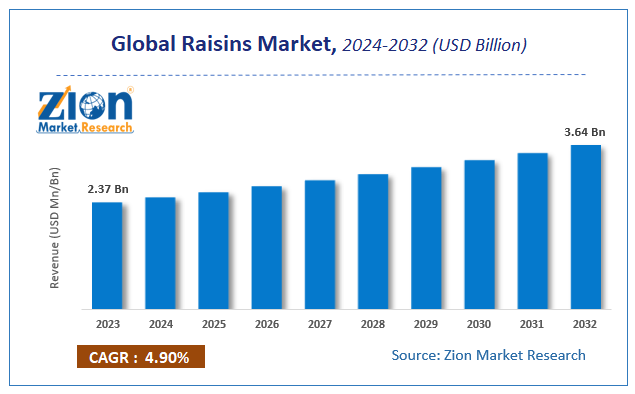
Raisins are among the top three dried fruits traded globally, alongside dates and apricots.
| A modern raisin processing plant is the backbone of the global dried fruit industry. From post-harvest grape handling to advanced sorting, grading, and packaging, processing plants determine final product quality, export eligibility, food safety, and market price.Global raisin production exceeds 1.3 million metric tons annually,Major raisin-producing countries such as Turkey, Iran, the USA, India, and Uzbekistan rely heavily on centralized processing plants to meet international quality and safety standards. |
Key Industry Statistics (H3)
-
Global raisin production exceeds 1.3 million metric tons annually
-
The global dried fruit market is valued at over USD 9 billion
-
Raisins account for approximately 45% of global dried grape trade
-
More than 70% of exported raisins pass through industrial processing plants before shipment
Major raisin-producing countries such as Turkey, Iran, the USA, India, and Uzbekistan rely heavily on centralized processing plants to meet international quality and safety standards.
Source references:
-
FAO – Food and Agriculture Organization
-
International Nut & Dried Fruit Council (INC)
-
USDA Specialty Crops Reports
What Is a Raisin Processing Plant? (H2)
A raisin processing plant is a specialized industrial facility designed to clean, sort, grade, stabilize, and package raisins for domestic consumption and export markets.
Unlike traditional sun-drying operations, modern plants use mechanized systems, optical technologies, and food-grade infrastructure to achieve high efficiency and consistent quality.
Core Objectives of a Processing Plant (H3)
-
Remove foreign materials and defects
-
Standardize size, color, and moisture
-
Improve food safety and shelf life
-
Add commercial value for export markets
-
Comply with international regulations (FDA, EU, Codex)
Raisin Processing Workflow Explained (H2)
1. Raw Material Reception & Pre-Cleaning (H3)
Fresh or dried grapes are received in bulk and undergo:
-
Vibratory screening
-
Air aspiration systems
-
Manual pre-inspection
This step removes stems, leaves, stones, and dust.
Specialized term: Foreign Matter Reduction (FMR)
2. Washing & Sanitation (H3)
Raisins are washed using food-grade stainless steel washing lines, often with:
-
Potable water
-
Ozonated or filtered water systems
-
Controlled antimicrobial solutions (where permitted)
This step reduces microbial load and improves hygiene.
3. Sorting & Grading Technology (H3)
This is the most critical phase in a modern raisin processing plant.
Advanced Sorting Systems Include:
-
Optical color sorters
-
Laser defect detection
-
X-ray scanners
-
Metal detectors
These technologies identify and remove:
-
Discolored raisins
-
Mold-affected fruit
-
Stones, glass, or metal fragments
Specialized term: Electronic Optical Sorting (EOS)
4. Size & Grade Classification (H3)
Raisins are graded based on:
-
Size (count per 100g)
-
Color uniformity
-
Moisture percentage (typically 13–15%)
-
Sugar content (Brix level)
Commercial grades such as Grade A, Select, Industrial, or Bakery Grade are prepared for different markets.
5. Packaging & Palletization (H3)
Processed raisins are packed using:
-
Vacuum packaging
-
Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP)
-
Bulk carton packaging (5–15 kg)
Retail formats range from 100g to 1kg, while bulk buyers prefer 10kg or 12.5kg cartons.
Quality Control & Food Safety Standards (H2)
A professional raisin processing plant operates under strict quality assurance (QA) and food safety systems.
Certifications Commonly Required (H3)
-
HACCP
-
ISO 22000
-
BRC / IFS
-
FDA Registration
-
EU Food Compliance
-
Organic Certification (if applicable)
“Processing plants with internationally recognized certifications gain immediate trust from importers and retailers.”
— Food Safety Consultant, Dried Fruit Industry
Raisin Processing Plants (H2)
Organic raisin processing requires segregated lines, enhanced traceability, and strict cleaning protocols.
Organic Processing Requirements (H3)
-
No chemical preservatives
-
Dedicated organic storage areas
-
Full batch traceability
-
Approved organic sanitation materials
Organic raisins command 20–40% higher prices than conventional products, making organic-certified processing plants highly attractive to global buyers.
Commercial Capacity & Investment Value (H2)
Typical Processing Plant Capacity (H3)
| Plant Size | Daily Capacity |
|---|---|
| Small | 5–10 tons/day |
| Medium | 20–40 tons/day |
| Large | 60–100+ tons/day |
High-capacity plants can process over 15,000 tons annually, serving both bulk commodity markets and premium retail brands.
Economic Impact (H3)
-
Processing increases raisin value by 25–60%
-
Reduces rejection rates in export markets
-
Enables private-label and branded sales
-
Improves price stability and margin control
Source: International Nut & Dried Fruit Council (INC)
Industry Quotes & Expert Opinions (H2)
“A raisin processing plant is not just a facility — it is a value-creation hub that transforms agricultural output into a globally tradable product.”
— Agribusiness Export Analyst
“Buyers today don’t just purchase raisins; they purchase processing credibility, traceability, and compliance.”
— Senior Procurement Manager, EU Food Importer
Export Markets Served by Processing Plants (H2)
Modern raisin processing plants supply:
-
🇪🇺 European Union
-
🇺🇸 United States
-
🇨🇦 Canada
-
🇨🇳 China
-
🇯🇵 Japan
-
🇦🇪 Middle East
Each market requires specific labeling, pesticide limits, and packaging standards, which only professional plants can meet consistently.
SEO Keywords for Raisin Processing Plant (H2)
To improve search visibility, integrate these keywords naturally:
-
Raisin processing plant
-
Raisin processing factory
-
Industrial raisin processing
-
Raisin sorting and grading line
-
Dried grape processing facility
-
Organic raisin processing plant
-
Raisin export processing unit
Conclusion: Why Raisin Processing Plants Matter (H2)
A modern raisin processing plant is essential for competing in today’s global dried fruit market. Through advanced technology, strict quality control, food safety compliance, and scalable capacity, these plants turn raw agricultural produce into high-value export commodities.
For investors, exporters, and buyers alike, partnering with a professional processing plant ensures consistent quality, regulatory compliance, and long-term commercial success.
Pistachio Different Grades Price
All Type Of Raisin
-
Golden Long Raisin
Golden Long Raisin also is known as Golden Raisin Jumbo or Kashmari Golden Raisin. As it is clear from its name the color of this raisin is golden. Raisins, in general, are dried grapes.
-
Green Raisins ( Jumbo Raisins ) wholesale price + analysis + sale offer
Green Raisins | Jumbo Raisins : Green Raisins also are known as Green Jumbo Raisin, Kashmari (Kashmiri) Green Raisins and Green Long Raisins. As it is clear from its name the color of this raisin is green. Raisins, in general,…
-
sultana raisin dark brown special wholesale price + analysis + sale offer
This kind is prepared by drying the fruit in full sun and results in a dark color.
-
Sultana Raisin Light Brown Special wholesale price + analysis + sale offer
Sultana Raisins Light Brown are dried Seedless grapes of the Vitis vinifera species. Customers also know this raisin as Malayer Raisin or Seedless Thompson. As it is clear from its name the color of this raisin is light brown. Farmers…
-
Golden Raisin Special wholesale price + analysis + sale offer
This kind is oven-dried and then sulfur is added to preserve its color.